Combining Data from two Tables
Cartesian Product
S1 = { a, b, c }
S2 = { 1, 2 }
S1 x S2 = { (a,1), (b,1), (c,1), (a,2), (b,2), (c,2) }
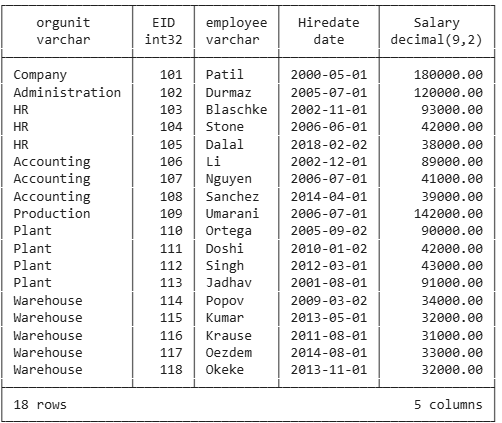
Cartesian Products on Tables
select *
from employee
cross join orgunit
order by orgunit.ouid, employee.eid;18 x 7 = 126 records
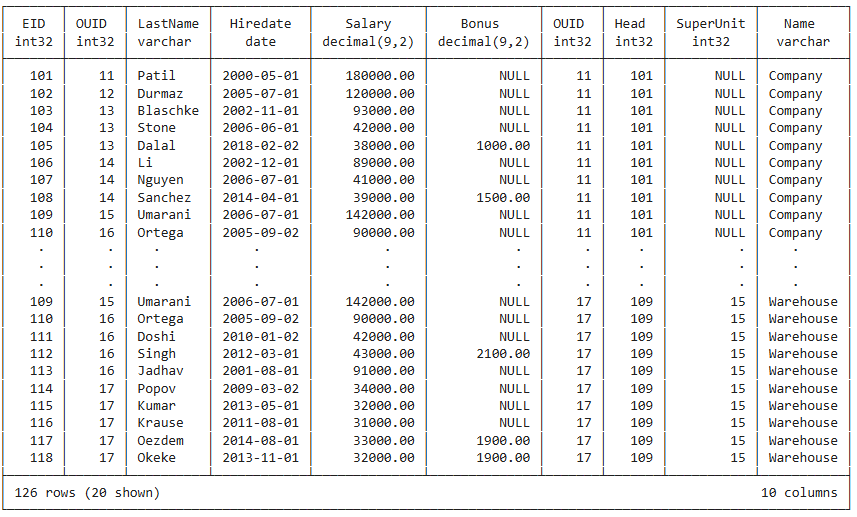
Filtering of the Cartesian Product
select *
from employee
cross join orgunit
where employee.ouid=orgunit.ouid
order by orgunit.ouid, employee.eid;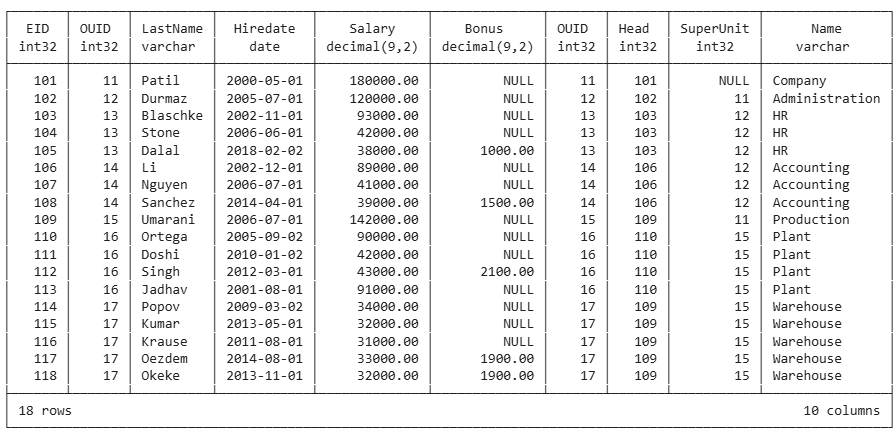
Inner Join
Long Version
select
orgunit.name as orgunit,
employee.eid, employee.lastname as employee, employee.hiredate, employee.salary
from employee
inner join orgunit on orgunit.ouid=employee.ouid
order by orgunit.ouid, employee.eid;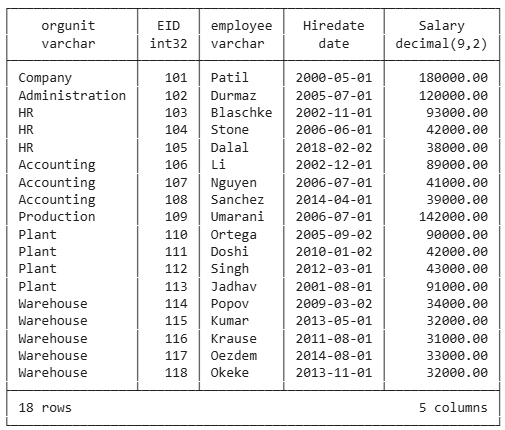
Short Version
short names for tables:
employee e
orgunit ou
inner join can be abbreviated to join
select
ou.name as orgunit,
e.eid, e.lastname as employee , e.hiredate, e.salary
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.ouid=e.ouid;Inner Working of Joins
Execute interactively
select *
from R
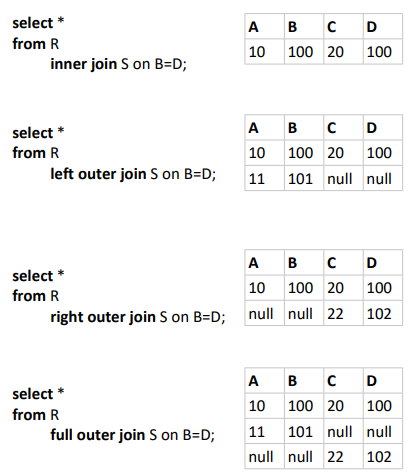
join S on B=D;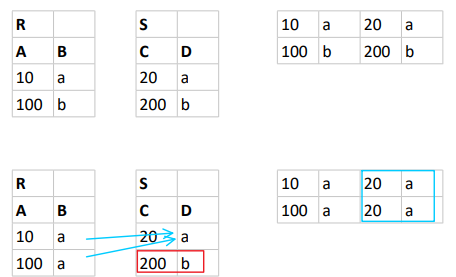
Red box:
Record doesn't appear in output due to no connection
Blue box:
Two occurrence of record due to two connections
Join of 3 Tables
Different order of tables don't matter
select p.title, e.lastname
from project p
join empproj ep on ep.pid=p.pid
join employee e on e.eid=ep.eid
order by p.title;select p.title, e.lastname
from empproj ep
join project p on p.pid=ep.pid
join employee e on e.eid=ep.eid
order by p.title;select p.title, e.lastname
from empproj ep
join employee e on e.eid=ep.eid
join project p on p.pid=ep.pid
order by p.title;Same result in all cases
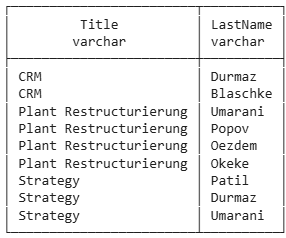
An arbitrary number of tables can be joined in one statement
Reflexive Join
select
parent.name as parent_unit,
child.name as child_unit
from orgunit parent
join orgunit child on child.superunit=parent.ouid
order by parent.ouid, child.ouid;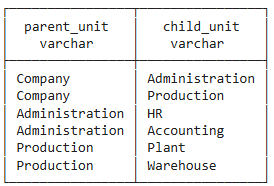
Twofold usage of same table requires different names of that table
Outer Join
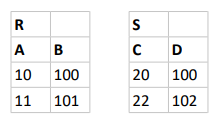
Tables
Joins
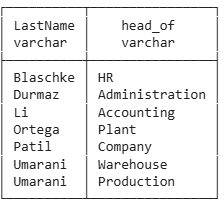
Heads and Non-Heads of Orgunits
Only Heads
select e.lastname, ou.name as head_of
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.head=e.eid
order by e.lastname;
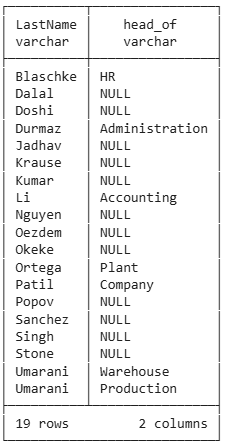
Left Outer Join keeps Non-Heads
select e.lastname, ou.name as head_of
from employee e
left join orgunit ou on ou.head=e.eid
order by e.lastname;
Only Non-Heads - Condition removes Heads
sselect e.lastname
from employee e
left join orgunit ou on ou.head=e.eid
where ou.name is null
order by e.lastname;
Same Result with Set Operation
elect e.lastname
from employee e
except
select e.lastname
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.head=e.eid
order by e.lastname;