Aggregation Functions
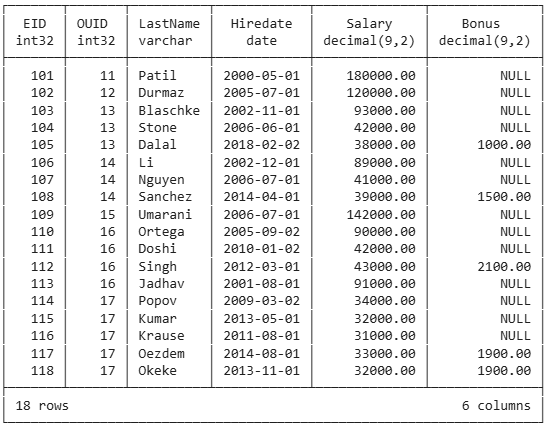
select
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
round(avg(salary)) as sal_avg,
min(salary) as sal_min,
max(salary) as sal_max,
count(*) as rec_count,
count(bonus) as bonus_count
from employee;
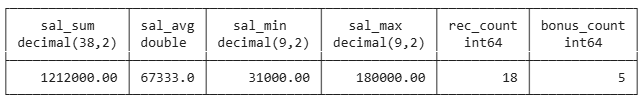
Grouping
Partitioning of detail data
Into different groups
According to grouping criterion, here OUID
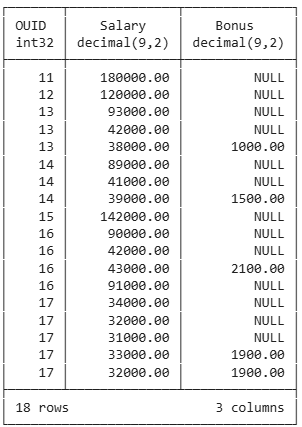
Resulting Groups
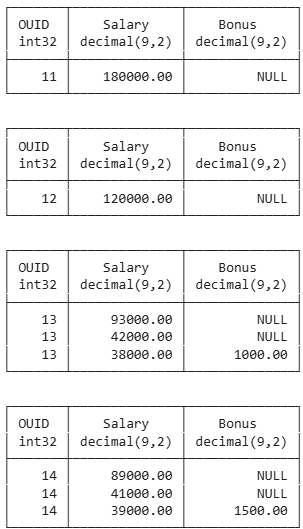
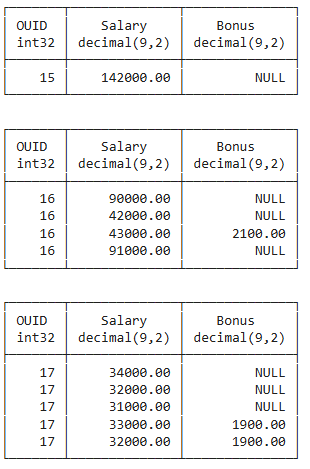
Application of aggregation functions on each individual group
select
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
round(avg(salary)) as sal_avg,
min(salary) as sal_min,
max(salary) as sal_max,
count(*) as rec_count,
count(bonus) as bonus_count
from employee
group by ouid;
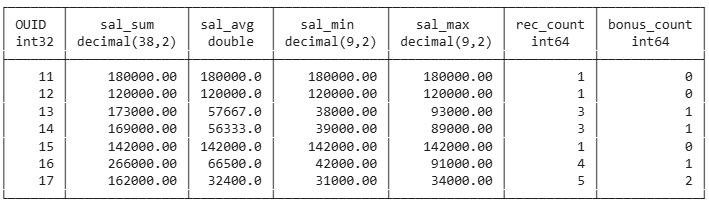
One record per group in the output
Aggregation Levels
select ouid,
sum(salary) as sal_sum
from employee
group by ouid
order by ouid;
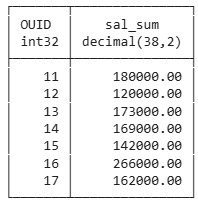
All output columns on same aggregation level
- OUID: part of group by
- sal_sum: aggregation function applied on column
select ouid, lastname,
sum(salary) as sal_sum
from employee
group by ouid
order by ouid;

Output columns on different aggregation levels
- OUID: aggregated
- lastname: on detail level (not possible)
- sal_sum: aggregated
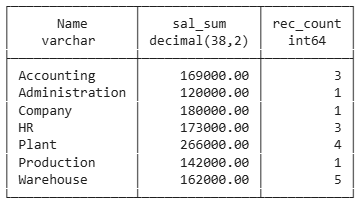
Grouping and Join

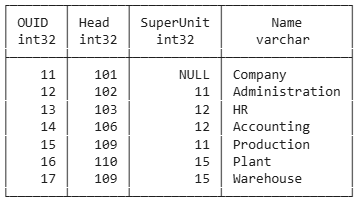
select ou.name,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.ouid=e.ouid
group by ou.name
order by ou.name;
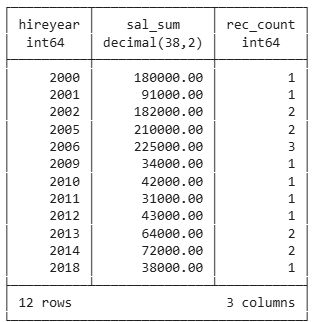
Grouping with Expressions 1

select
extract(year from hiredate) as hireyear,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by hireyear
order by hireyear;
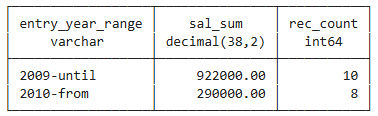
Grouping with Expressions 2

select
case
when hiredate >= '2010-01-01' then '2010-from'
when hiredate >= '2000-01-01' then '2009-until'
end as entry_year_range,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by entry_year_range
order by entry_year_range;
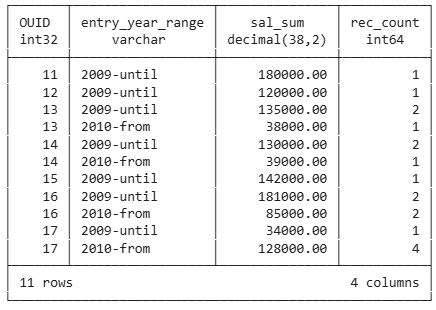
Grouping with several Columns

select
ouid,
case
when hiredate >= '2010-01-01' then '2010-from'
when hiredate >= '2000-01-01' then '2009-until'
end as entry_year_range,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by ouid, entry_year_range
order by ouid, entry_year_range;
order by entry_year_range;
Value Combinations as Groups
Grouping according to one Column
select
case
when hiredate >= '2010-01-01' then '2010-from'
when hiredate >= '2000-01-01' then '2009-until'
end as entry_year_range,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by entry_year_range
order by entry_year_range;
Grouping according to two Columns
select
ouid,
case
when hiredate >= '2010-01-01' then '2010-from'
when hiredate >= '2000-01-01' then '2009-until'
end as entry_year_range,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by ouid, entry_year_range
order by ouid, entry_year_range;
New Groups according to Value Combinations


Adding a column in grouping usually leads to new groups
Grouping with dependent Columns
Bases Tables


Invalid Gouping
Select ou.ouid, ou.name, sum(salary) as sal_sum
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.ouid=e.ouid
group by ou.ouid
order by ou.ouid;

Dependent Columns
Every time OUID has the same value, also name has the same value
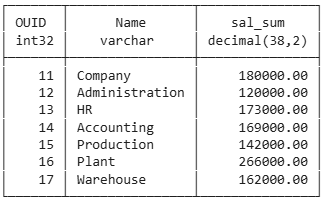
Valid Gouping
Column ou.name added to group by
No new combinations, because ou.name depends on ou.OUID
select ou.ouid, ou.name, sum(salary) as sal_sum
from employee e
join orgunit ou on ou.ouid=e.ouid
group by ou.ouid, ou.name
order by ou.ouid;
Conditions on Group Level
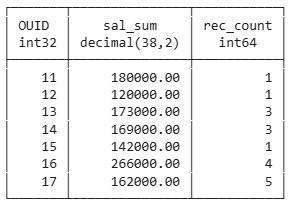
Without Condition on Group Level
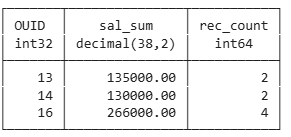
select ouid,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by ouid
order by ouid;
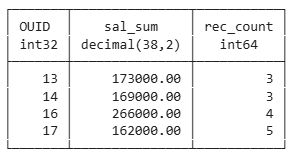
Same Query With Condition on Group Level
Keyword having
select ouid,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by ouid
having count(*) > 1
order by ouid;
Reduction of Number of Groups
Conditions on Detail Level and Group Level
Without Condtition on Detail Level
select ouid,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
group by ouid
having count(*) > 1
order by ouid;
Same Query With Condition on Detail Level
Keyword where
select ouid,
sum(salary) as sal_sum,
count(*) as rec_count
from employee
where salary > 40000
group by ouid
having count(*) > 1
order by ouid;
Reduction of Number of Groups and Number of Records per Group

Structure of a Query with Grouping
select
from
where
group by
having
order by